kcnt1 epilepsy life expectancy
This is the Epilepsiome page on KCNT1 a gene primarily associated with two distinct genetic epilepsy syndromes namely Migrating Partial Seizures of Infancy MPSI and Autosomal Dominant Nocturnal Frontal Lobe Epilepsy ADNFLE. Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures EIMFS initially described in 1995 Coppola et al 1995 is a rare developmental epileptic encephalopathy with an estimated incidence of 011 per 100 000 Lim et al 2016The key features of this syndrome include focal seizures onset in the first 6 months of life with a specific EEG ictal pattern recognized as.
Kcnt1 This Is What You Need To Know Beyond The Ion Channel
Also known as migrating partial seizures in infancy autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy and other types of early onset epileptic encephalopathies EOEEs.

. Mutations in the KCNT1 gene have been found in several people with autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy ADNFLE which causes seizures that usually occur at night nocturnally while an affected person is sleeping. Pathogenic variants identified in KCNT1-related epilepsy cluster in the S5 transmembrane and the Regulators of Potassium RCK domains of the channel protein. Epilepsy is a type of neurological disorder known for causing seizures.
Variants in KCNT1 encoding a sodium-gated potassium channel subfamily T member 1 have been associated with a spectrum of epilepsies and neurodevelopmental disorders. SAN DIEGO and WASHINGTON May 26 2020 PRNewswire The KCNT1 Epilepsy Foundation LunaPBC and Genetic Alliance today announced a program to assemble a patient-led drug discovery community to study disease. The non-working variant can either be inherited from either parent or be a new change de novo in the affected child.
The mission of the KCNT1 Epilepsy Foundation is to support the development of treatments and find an eventual cure for KCNT1-related epilepsies. These range from familial autosomal dominant or sporadic sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy to epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures EIMFS and include developmental and. EIMFS is characterized by seizures typically focal and asynchronous beginning in the first six months of life with associated developmental plateau.
KCNT1 mutations have been found in epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures EIMFS. In 2015 KCNT1 is not getting any less mysterious. Regular physical and occupational therapy in early life is very important including therapies that involve early weight-bearing.
Recurrent seizures begin before the age of 6 months but commonly start within a few weeks of birth. These range from familial autosomal dominant or sporadic sleep-related hypermotor epilepsy to epilepsy of infancy with migrating f. Figure generated from an image drawn using Protter open-source software Omasits et al 2014.
The majority of affected individuals represent simplex cases ie a single occurrence in a family resulting from a de novo KCNT1 pathogenic variantThe proportion of cases caused by a de novo pathogenic variant varies by phenotypeAll individuals diagnosed with KCNT1-related. In addition the very same mutations can result in a severe from of frontal lobe epilepsy with prominent psychiatric features. Although affected individuals may develop normally at first.
The seizures do not respond well to treatment. Heron et al 2012. KCNT1 mutations in MMFSI.
KCNT1-related developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. With early onset KCNT1 related epilepsy children often start out very hypotonic floppy in the first year of life. KCNB1 encephalopathy is an autosomal dominant genetic condition meaning that only one non-working copy of the gene leads to disease.
Program incorporates patient-driven study to inform research and drug development for KCNT1-related epilepsy. Autosomal dominant pathogenic variants in KCNT1 encoding the sodium-activated potassium channel are identified in a wide spectrum of epileptic disorders with variable age at onset and cognitive outcomeThese include severe early-onset epileptic encephalopathies such as Ohtahara and West syndromes 12 and epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal. KCNT1-related epilepsy is most often associated with two phenotypes.
Several mutation hotspots and recurrent mutations in KCNT1 are emerging. Between 1970 and 1980 patients diagnosed with symptomatic epilepsy had a substantially greater reduction in life expectancy 74 years in women and 72 years in men than people diagnosed with idiopathic epilepsy 55 years in women and 52 years in men and people diagnosed with cryptogenic epilepsy 18 years in women. It is associated with both ADNFLE and a severe epileptic encephalopathy called epilepsy in infancy with migrating focal seizures Barcia et al 2012.
Ever since its discovery in 2012 KCNT1 mutations are increasingly recognized in severe early onset epilepsies. Methods Patient recruitment WerecruitedpatientswithEIMFSn31toaresearchstudy investigating the genetic basis of early-onset epileptic en-cephalopathy EOEE between 2011 and 2016 following an earlier national surveillance study4 Inclusion criteria were epilepsy with onset at. Variants in KCNT1 encoding a sodium-gated potassium channel subfamily T member 1 have been associated with a spectrum of epilepsies and neurodevelopmental disorders.
KCNT1-related frontal lobe epilepsy. The risk of a patient passing the non-working gene to an offspring is 50 for each pregnancy. KCNT1-related epilepsies fall into two broad categories.
We performed KCNT1-targeted next-generation sequencing 207 samples andor whole. These seizures can be sporadic and occur without warning or they might be chronic and occur on a regular basis. In addition to seizures most affected individuals with KCNT1 gene mutations have psychiatric problems such as aggression.
Malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy MMPSI is a severe form of epilepsy that begins very early in life. It remains a gene that causes a very rare but distinct catastrophic epilepsy of childhood. Seizures beginning in infancy not associated with a fever may be the first indication of KCNT1-related epilepsySeizures from some KCNT1-related epilepsies may begin in the first year of life and even within days of birth.
We have a patient registry with over 100 children a sponsored natural history study and will be creating biobank. KCNT1 encodes a sodium-activated potassium channel that is widely expressed in the brain particularly the frontal cortex. Epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures EIMFS and autosomal dominant nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy ADNFLE.
In these children seizures typically begin in the first days or months of life. This might involve things like a gait trainer or a stander and this can help with bone health children. KCNT1-related epilepsy is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
MMFSI also known as epilepsy of infancy with migrating focal seizures is an early-onset epileptic encephalopathy EOEE characterised by migrating multifocal seizures with onset before 6 months of age7 Seizures are intractable to antiepileptic drugs and patients experience severe psychomotor developmental delay7 Barcia.
Baby Diagnosed With Rare Form Of Epilepsy That Leaves Him Suffering Up To 50 Seizures A Day Chronicle Live

Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy For Kcnt1 Encephalopathy Biorxiv
Kcnt1 This Is What You Need To Know Beyond The Ion Channel

Baby Diagnosed With Rare Form Of Epilepsy That Leaves Him Suffering Up To 50 Seizures A Day Chronicle Live

In Silico Model Reveals The Key Role Of Gaba In Kcnt1 Epilepsy In Infancy With Migrating Focal Seizures Kuchenbuch 2021 Epilepsia Wiley Online Library

Kcnt1 Wild Type Wt And Mutant Currents Recorded In Xenopus Oocytes Download Scientific Diagram

Kcnt1 An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ethan S Strength Unity Of White Mountains

A Pedigrees Of Families 1 And 2 With Kcnt1 Mutations Diagonal Lines Download Scientific Diagram

In Silico Model Reveals The Key Role Of Gaba In Kcnt1 Epilepsy In Infancy With Migrating Focal Seizures Kuchenbuch 2021 Epilepsia Wiley Online Library

Kcnt1 An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
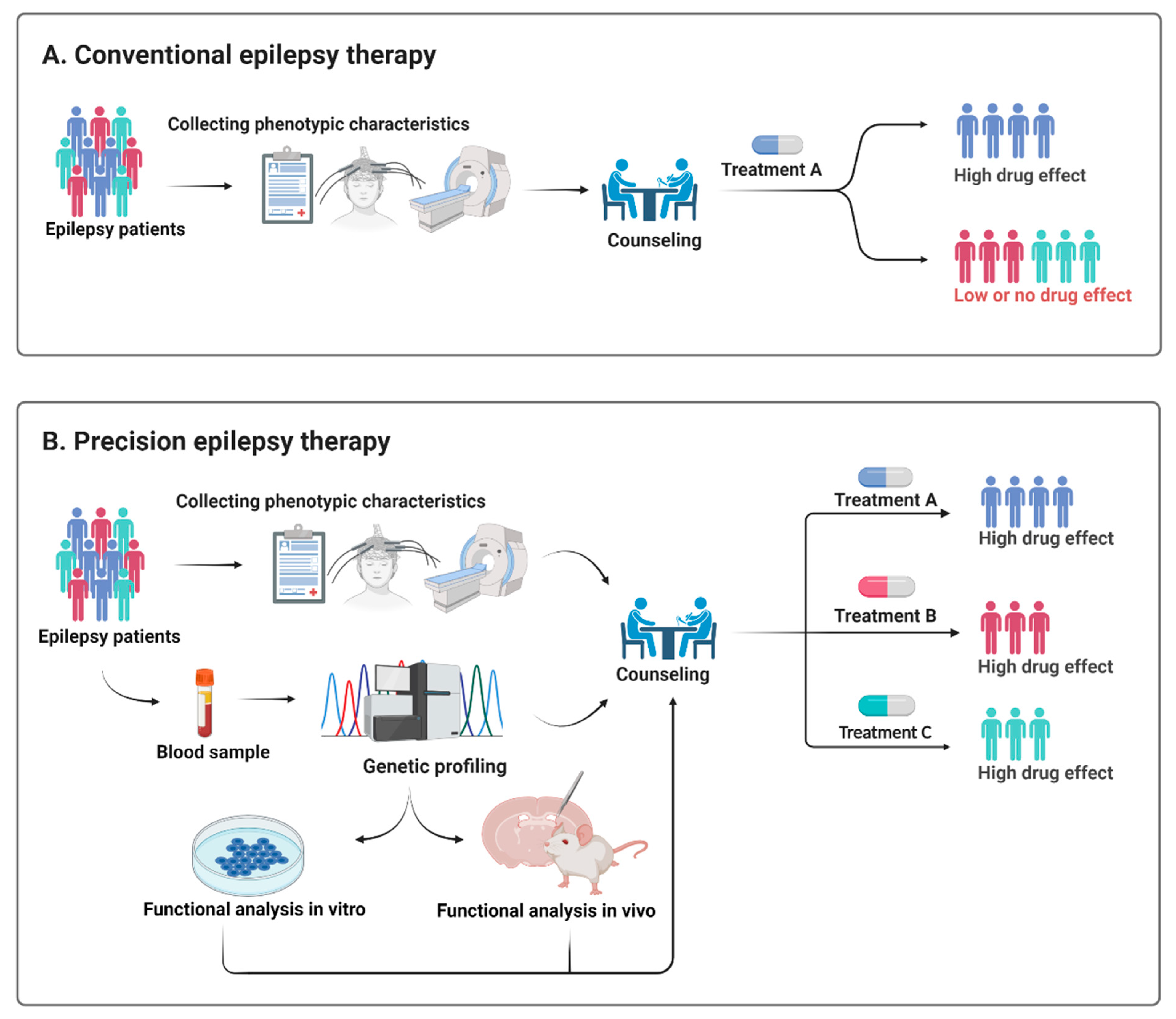
Genes Free Full Text Epilepsy Syndromes In The First Year Of Life And Usefulness Of Genetic Testing For Precision Therapy Html

Resources For Parents Of Children With Kcnt1 Home Kcnt1 Epilepsy Foundation

Model Of The Kcnt1 Channel Protein And Showing Locations Of Mutations Download Scientific Diagram
Resources For Parents Of Children With Kcnt1 Home Kcnt1 Epilepsy Foundation

Ethan S Strength Unity Of White Mountains
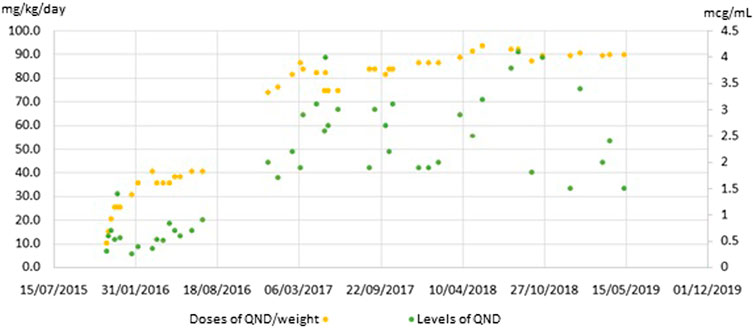
Frontiers Case Report Of Novel Genetic Variant In Kcnt1 Channel And Pharmacological Treatment With Quinidine Precision Medicine In Refractory Epilepsy Pharmacology

Resources For Parents Of Children With Kcnt1 Home Kcnt1 Epilepsy Foundation